The object’s properties are specified in the Object-Planar dialog. These properties include a unique object label, description, wireframe color, labeling options, and surface reflectances. When the object is initially specified, the surfaces is created as a two sided object with color and reflectance. You may edit the object, after creation, to assign a different reflectance (color) to it, if desired.
Create a triangular planar object
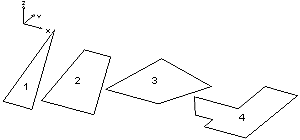
Triangular planar objects are created in Plan view or Elevation view and can be reflective on one or both sides. They can also be transparent. Each vertex on the triangle may have a different Z coordinate, if desired.
- From the Add
menu select Object - Planar, or
from the Rooms/Objects Toolkit select
 .
. - Specify a unique label for the object up to 32 characters long. The default label will be Object_1. Unless changed, subsequent labels will be Object_2, Object_3, etc. If a number is used for the label, subsequent labels will be incremented accordingly.
- If desired, a description may be entered, up to 80 characters long. Meaningful descriptions including size and color will be useful for schedules.
- The object will be created in AGi32 using the selected Wire Frame Color. This color is not used in AGi32's Render mode, it is only used to represent the object 's shape in the graphics window. By default, this color is blue. To change it, click in the color cell. The Color dialog will appear for your use.
- If surface labeling is desired, click on the Labeling button. A separate dialog will appear for specification of text labels for the object and/or its surfaces.
- The planar surface is assigned a color. You may change the reflectance by simply typing a new value in the Reflectance cell. You may change the surface color and its corresponding reflectance by clicking in the Color cell. The Color Selection dialog will appear allowing you to select surface colors based on user defined reflectances.
- You may assign a texture to the surface by clicking in the Texture cell. The Select Texture dialog will appear so that you may choose a texture from the Textures database. Alternately, you may browse for a texture anywhere on your system or assign a texture already in use on another surface in the job file. Once the desired texture is selected, you'll determine how the texture should be applied to the surface. Textures may be stretched across the entire surface, applied in a grid pattern or assigned a Static size (representing real dimensions) and tiled on the surface accordingly. In addition, you may opt to rotate the texture on the surface.
To delete a texture from the surface, Ctrl-click in the Texture cell and select the Delete key on your keyboard. When a texture is deleted from a surface, its correlated color and reflectance are used as the current color and reflectance.
- To apply additional surface properties (such as Texture, Transmittance, Transparency, Luminance, Specularity, Color Bleed control or surface specific Mesh Levels) to any of the object surfaces, you must first position the object in the environment. Then, either Edit the object and select the Surface Edit button in the Edit dialog or use the Edit Surface command to select the object.
- Click on the radio button adjacent to Triangle.
- You may specify the Z coordinates of the top and bottom before exiting to the graphics window, if desired.
- Click OK to return to the graphics window and
locate the first point of the triangle. Before clicking in the first point,
you will have the opportunity to change the Z coordinate of the bottom,
if desired (Plan View). Move the cursor into the Z-Coordinates Bottom
dialog and enter the appropriate value. Click the left mouse button.
- Note: If the Z-Coord value is not equal to zero,a warning icon will be displayed to alert the user to this condition.
- Drag the cursor to the second point on the triangle. You may change the Z coordinate of the second point if desired by moving the cursor into the Z-Coord text box and entering the Z value. Left click the mouse button at the vertex location.
- Drag the cursor to the third point on the triangle. You may change the Z coordinate of the top at this time by moving the cursor into the Z-Coord text box and entering the appropriate value in Plan view. Notice that you are informed whether the surface is reflecting up or down. You may flip the reflective side in the opposite direction by clicking the F5 key. Click the left mouse button again to locate the third point.
Create a quadrilateral planar object
Quadrilateral (four sided) planar objects can be created in Plan view or Elevation view and can be reflective on one or both sides, or transparent. In Plan View, you may create a non parallel quadrilateral unless the object is tilted (Ztop ¹ Zbottom). In the case of a tilted object, a trapezoid is created (bottom and top are parallel). In Elevation view, you may create a quadrilateral because the planar object is inherently restricted to the specified plane.
- From the Add
menu select Object - Planar, or
from the Rooms/Objects Toolkit select
 .
. - Specify a unique label for the object up to 32 characters long. The default label will be Object_1. Unless changed, subsequent labels will be Object_2, Object_3, etc. If a number is used for the label, subsequent labels will be incremented accordingly.
- If desired, a description may be entered, up to 80 characters long. Meaningful descriptions including size and color will be useful for schedules.
- The object will be created in AGi32 using the selected Wire Frame Color. This color is not used in AGi32's Render mode, it is only used to represent the object's shape in the graphics window. By default, this color is blue. To change it, click in the color cell. The Color dialog will appear for your use.
- If surface labeling is desired, click on the Labeling button. A separate dialog will appear for specification of text labels for the object and/or its surfaces.
- The planar object is assigned a color and reflectance. You may change the surface colors and their corresponding reflectances by clicking in the color cell. The Color Selection dialog will appear allowing you to select surface colors based on user defined reflectances.
- You may assign a texture to the surface by clicking in the Texture cell. The Select Texture dialog will appear so that you may choose a texture from the Textures database. Alternately, you may browse for a texture anywhere on your system or assign a texture already in use on another surface in the job file. Once the desired texture is selected, you'll determine how the texture should be applied to the surface. Textures may be stretched across the entire surface, applied in a grid pattern or assigned a Static size (representing real dimensions) and tiled on the surface accordingly. In addition, you may opt to rotate the texture on the surface.
To delete a texture from the surface, Ctrl-click in the Texture cell and select the Delete key on your keyboard. When a texture is deleted from a surface, its correlated color and reflectance are used as the current color and reflectance.
- To apply additional surface properties (such as Texture, Transmittance, Transparency, Luminance, Specularity, Color Bleed control or surface specific Mesh Levels) to any of the object surfaces, you must first position the object in the environment. Then, either Edit the object and select the Surface Edit button in the Edit dialog or use the Edit Surface command to select the object.
- Click on the radio button adjacent to Quadrilateral/Trapezoid.
- You may specify the Z coordinates of the top and bottom before exiting to the graphics window, if desired.
- Click Ok to return to the graphics window and locate the first point of the object. Before clicking in the first point, you will have the opportunity to change the Z coordinate of the bottom, if desired (Plan View). Move the cursor into the Z-Coord text box and enter the appropriate value. Click the left mouse button.
- Drag the cursor to the second point on the object 's bottom and left click again.
- Drag the cursor to the third point on the planar object. You may change the Z coordinate of the top at this time by moving the cursor into the Z-Coord text box and entering the appropriate value (Plan View). Notice that you are informed whether the surface is reflecting up or down. You may flip the reflective side in the opposite direction by clicking the F5 key. Click the left mouse button again to locate the third point.
- Drag the cursor to the fourth point on the quadrilateral and left click once more. If the planar object is sloping in Plan view, you will be restricted to specifying a line parallel to the bottom. You may not flip or change the Z coordinate at this time.
Create a polygon planar object
Planar objects with a user defined polygon boundary can be reflective on one or both sides and can be created in Plan view, Rotated Plan view and Elevation view. For polygons created in Plan view, each vertex on the polygon must be located at the same Z-coordinate but the entire planar polygon may lie at any elevation. For polygons created in Elevation view, all vertices must lie in the current elevation plane.
- From the Add
menu select Object - Planar. or
from the Rooms/Objects Toolkit select
 .
. - Specify a unique label for the object up to 32 characters long. The default label will be Object_1. Unless changed, subsequent labels will be Object_2, Object_3, etc. If a number is used for the label, subsequent labels will be incremented accordingly.
- If desired, a description may be entered, up to 80 characters long. Meaningful descriptions including size and color will be useful for schedules.
- The object will be created in AGi32 using the selected Wire Frame Color. This color is not used in AGi32's Render mode, it is only used to represent the object 's shape in the graphics window. By default, this color is blue. To change it, click in the color cell. The Color dialog will appear for your use.
- If surface labeling is desired, click on the Labeling button. A separate dialog will appear for specification of text labels for the object and/or its surfaces.
- The planar object is assigned a color and reflectance. You may change the surface colors and their corresponding reflectances by clicking in the color cell. The Color Selection dialog will appear allowing you to select surface colors based on user defined reflectances.
- You may assign a texture to the surface by clicking in the Texture cell. The Select Texture dialog will appear so that you may choose a texture from the Textures database. Alternately, you may browse for a texture anywhere on your system or assign a texture already in use on another surface in the job file. Once the desired texture is selected, you'll determine how the texture should be applied to the surface. Textures may be stretched across the entire surface, applied in a grid pattern or assigned a Static size (representing real dimensions) and tiled on the surface accordingly. In addition, you may opt to rotate the texture on the surface.
To delete a texture from the surface, Ctrl-click in the Texture cell and select the Delete key on your keyboard. When a texture is deleted from a surface, its correlated color and reflectance are used as the current color and reflectance.
- To apply additional surface properties (such as Texture, Transmittance, Transparency, Luminance, Specularity, Color Bleed control or surface specific Mesh Levels) to any of the object surfaces, you must first position the object in the environment. Then, either Edit the object and select the Surface Edit button in the Edit dialog or use the Edit Surface command to select the object.
- Click on the radio button adjacent to Polygon.
- You may specify the Z coordinates of the polygon bottom before exiting to the graphics window, if desired. This is active only when creating the object in Plan view.
- Creation Method: Choose whether to manually create boundary lines of planar object or choose existing lines as the boundary line.
- Planar object will always be flat in Plan View.
- If a tilted line is selected, polygon will be projected down to and created at lowest Z coordinate elevation.
- Click Ok. Follow the steps below depending on the selected creation method:
|
Specify a Polygon Manually |
Create Planar Object Polygon from Drawing Entities |
|---|---|
|
Notes:
Caveats:
|